Investors who bought Nvidia (NASDAQ: NVDA) stock immediately after the DeepSeek-related market crash on January 27, 2025 realized significant gains.
For example, if you invested $1,000 on the day of the crash at $118 per share, you would have acquired approximately 8.47 shares. By January 23, 2026, if NVIDIA trades at $184 per share, that position will be worth approximately $1,580, reflecting a gain of $580 and a 58% gain.
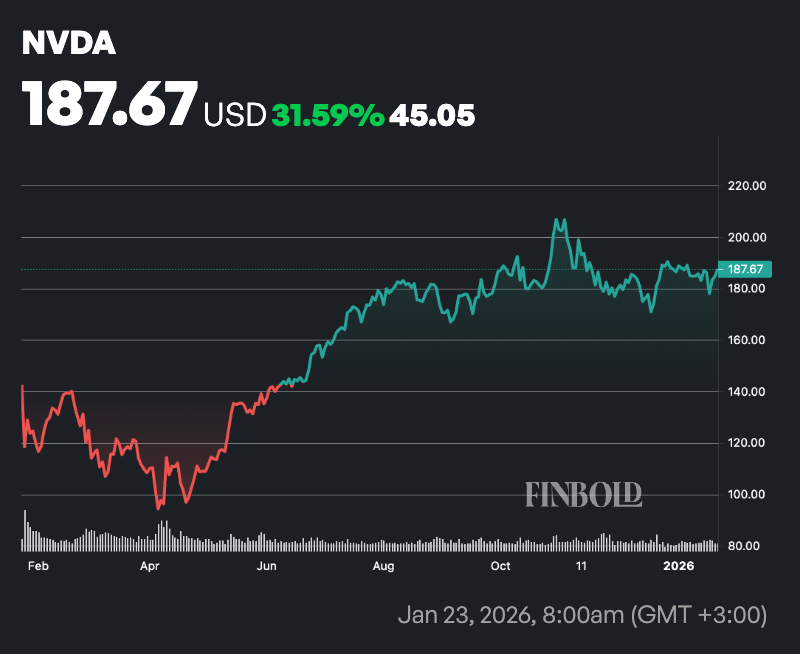
The DeepSeek market crash followed a sharp decline in technology stocks triggered by the release of an advanced AI model from Chinese startup DeepSeek.
The company’s low-cost, high-performance models, including the R1 and V3, sparked investor concerns about weakening U.S. leadership in AI and waning demand for expensive hardware from companies like Nvidia, prompting widespread selling across the sector.
Nvidia was hit hardest by the selloff, dropping nearly 17% in a single transaction, shedding about $600 billion in market value, the largest single-day loss in Wall Street history. The broader market also fell, with the Nasdaq down 3.1%.
Nvidia stock recovery path
In fact, the U.S. tech giant began its recovery the next day, rebounding nearly 9% as investors decided the selloff was an overreaction.
In the months that followed, the stock rose steadily on sustained demand for high-performance GPUs in AI training and inference.
The strong quarterly results highlighted the resilience of data center revenues, supported by partnerships with major US technology companies to expand their AI infrastructure.
At the same time, chipmakers’ advances in chip design and software ecosystems have further strengthened their position, and sentiment has shifted to the view that more efficient AI models will increase overall adoption rather than reduce hardware demand.
Meanwhile, the enthusiasm for DeepSeek has died down. Subsequent model updates were gradual and limited access to advanced computing, exacerbated by U.S. export controls, which delayed major releases such as the anticipated R2 model.
Geopolitical tensions also prevented Western companies from adopting Chinese AI solutions, limiting their commercial impact.
At the same time, U.S. competitors such as OpenAI and Google have strengthened their ecosystem with integrated tools and enterprise-grade reliability, reducing DeepSeek’s cost-conscious appeal.
Featured image via Shutterstock


