Amid the crypto market stagnation caused by October’s historic market crash, the Ethereum Layer 1 blockchain gas fee fell to just 0.067 Gwei on Sunday.
According to Etherscan, at the time of writing, the average price for performing a swap on Ethereum is just $0.11, selling a non-fungible token (NFT) costs a fee of $0.19, bridging a digital asset to another blockchain network costs users $0.04, and on-chain borrowing costs $0.09.
Ethereum network transaction fees reached a recent high of 15.9 Gwei on October 10, during a market flash crash that caused the value of some altcoins to fall by more than 90% within 24 hours.
However, by October 12, the fee had fallen to just 0.5 Gwei and remained well below 1 Gwei for most throughout October and November.
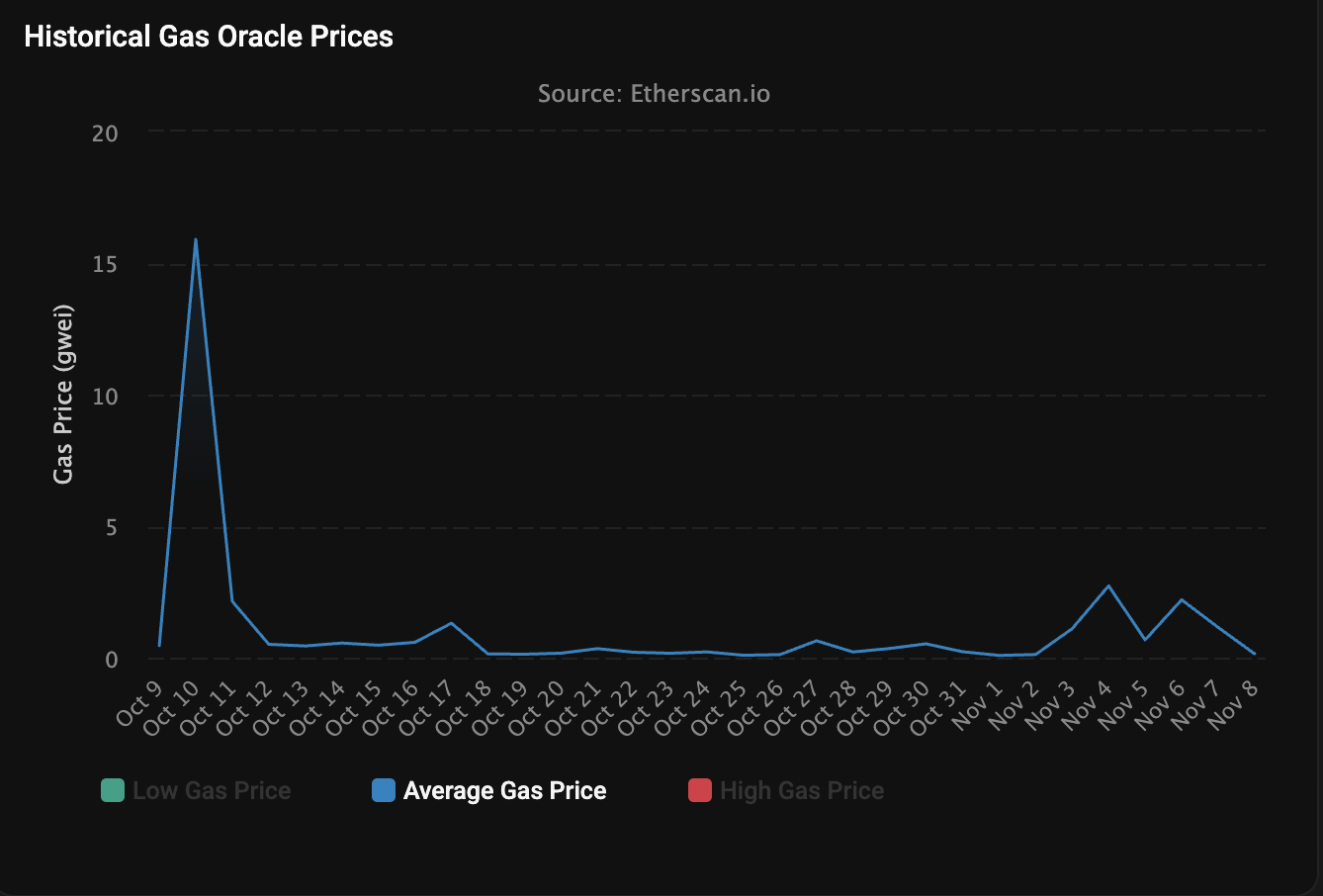
Ethereum layer 1 gas price last month. sauce: ether scan
Investors and traders can take advantage of low transaction fees and perform on-chain transactions at the base layer. However, analysts and crypto industry executives have warned that excessively low fees could cause problems for the Ethereum ecosystem.
Related: Ethereum fees remain close to a penny as daily transactions exceed 1.6 million
Ethereum base layer revenue is decreasing after 2024
During the 2021 bull market, Ethereum Layer 1 transaction fees could cost users $150 or more during times of network congestion.
However, after the Ethereum Dencun upgrade in March 2024 lowered transaction fees on Ethereum’s Layer 2 scaling network, fees shrunk significantly and Ethereum’s revenue decreased by 99%.
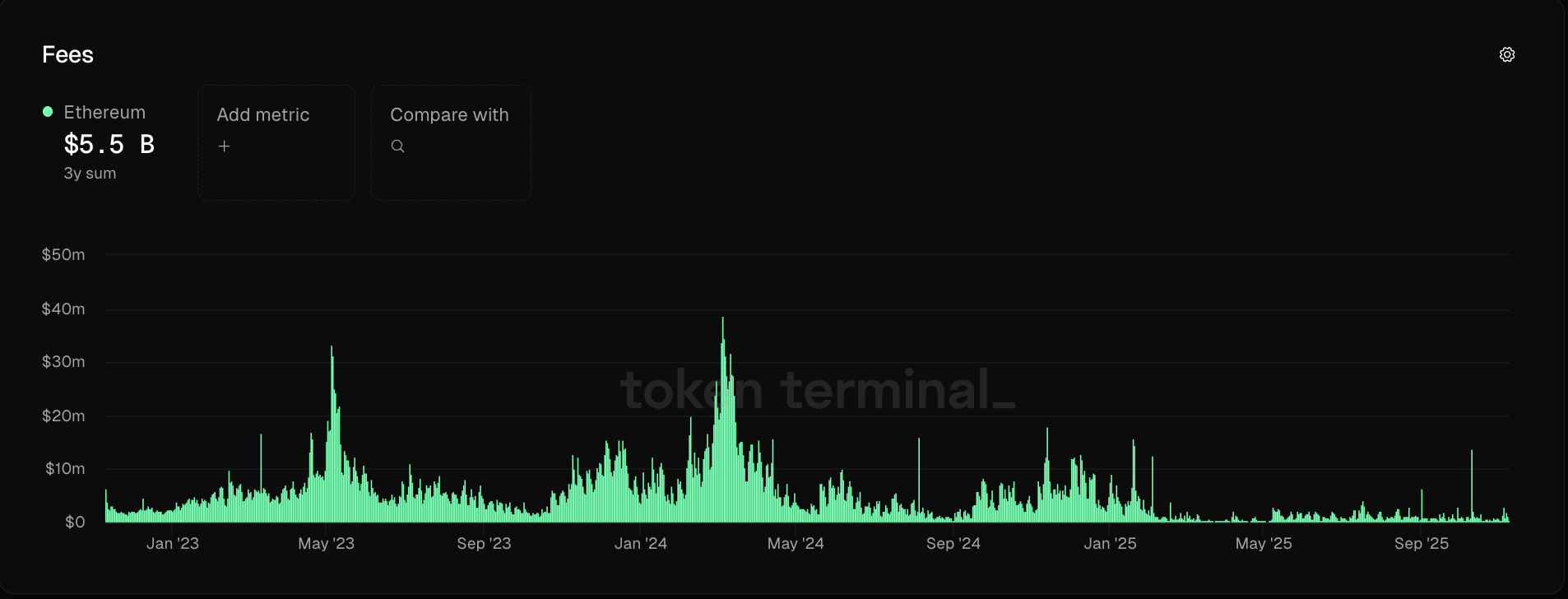
Ethereum Layer 1 Network Fees from 2023 to 2025. sauce: token terminal
Critics say low network fees are unsustainable for any blockchain network, creating both financial and security challenges due to a lack of income to incentivize validators and miners to process transactions and secure the blockchain.
Fees change based on user demand, so low fees or revenue may also indicate that users are moving away from a particular blockchain network.
According to a study by crypto exchange Binance, Ethereum in particular is choosing a scaling strategy that relies on an ecosystem of separate Layer 2 networks, which is a double-edged sword.
While the Layer 2 network allows Ethereum to scale and compete with new high-throughput chains, the Layer 2 network cannibalizes revenue from the base layer and creates further competition for Ethereum within its own ecosystem.
magazine: How Ethereum Finance Companies Can Spark “DeFi Summer 2.0”


